OTSON Technologies Corp. is a well-known provider of cutting-edge paint shop solutions for various industrial and commercial markets. Our extensive range of products and services are designed to help our clients improve their painting processes, reduce costs, and increase overall efficiency. With years of experience as a reputable manufacturer, we take pride in delivering high-quality products and services to meet the needs of our valued customers.
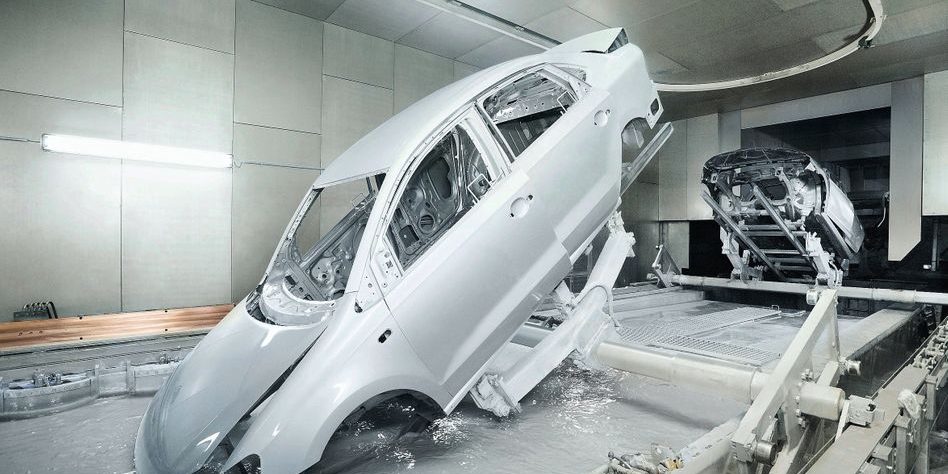
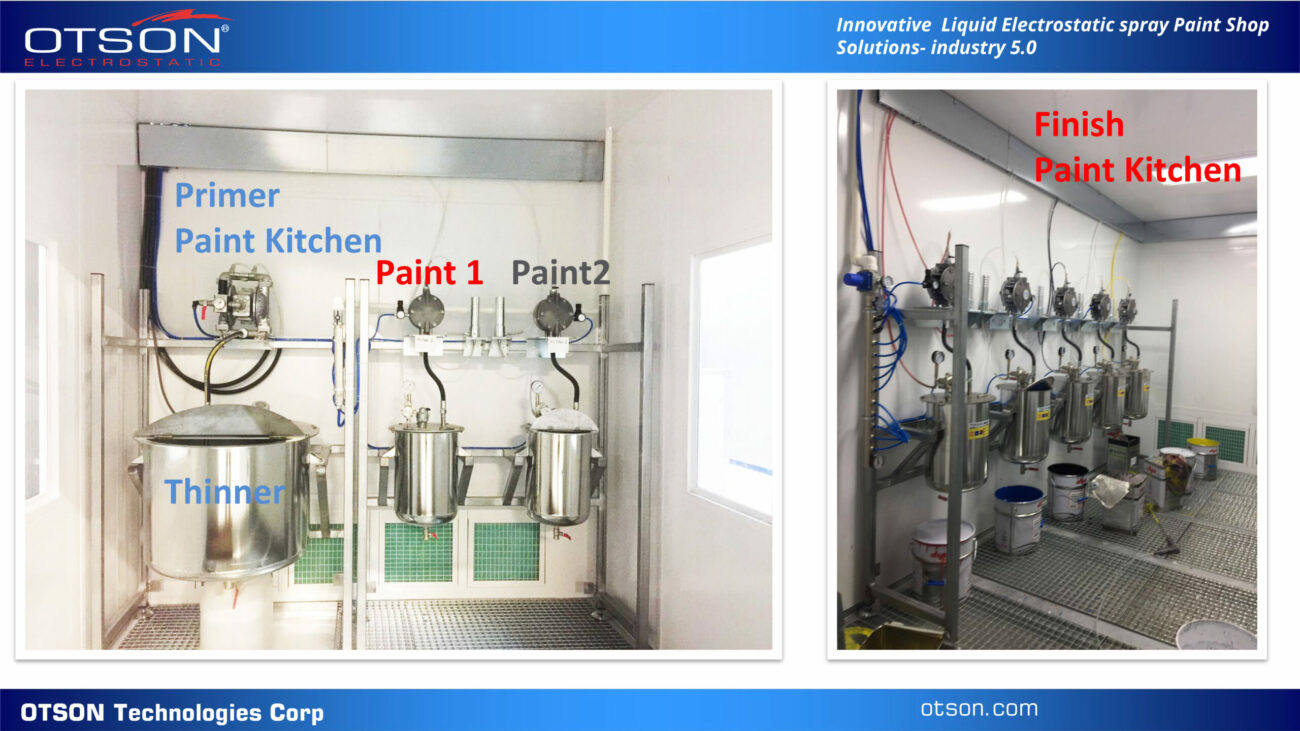
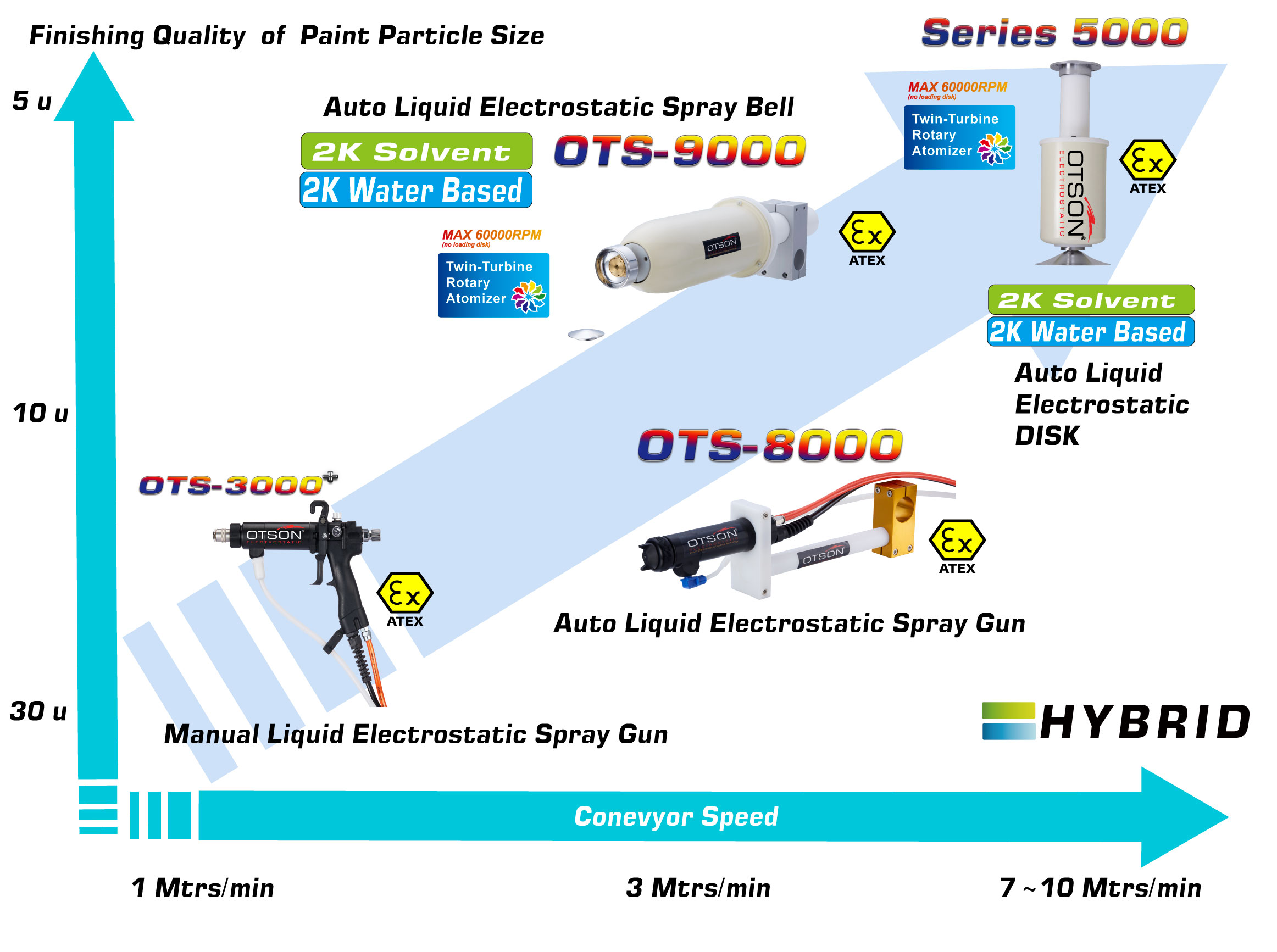
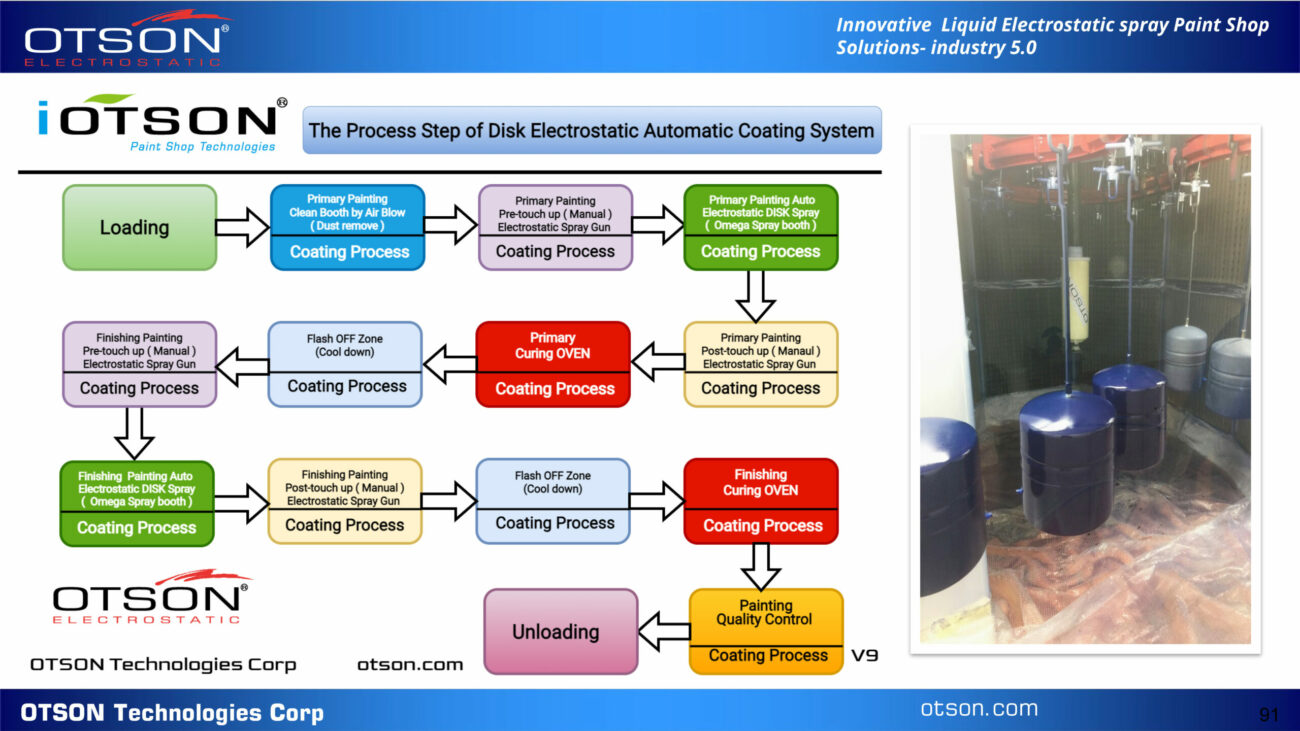
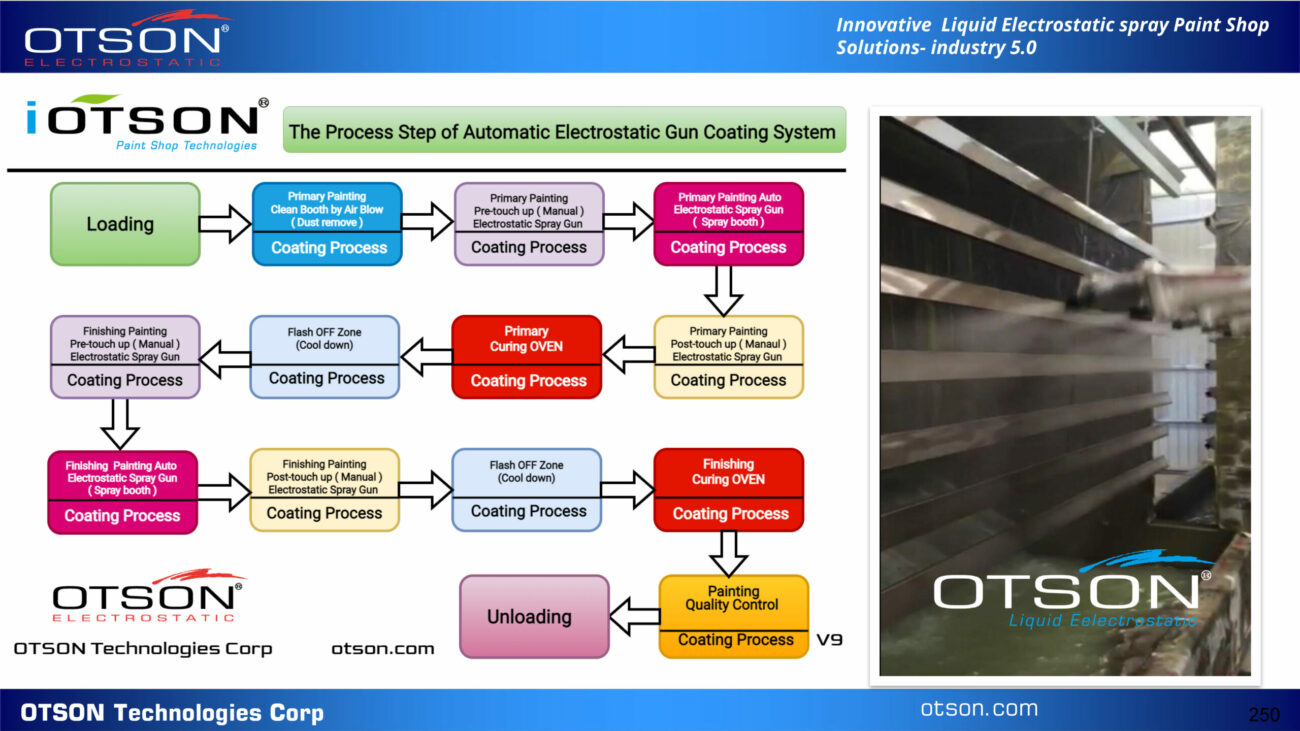
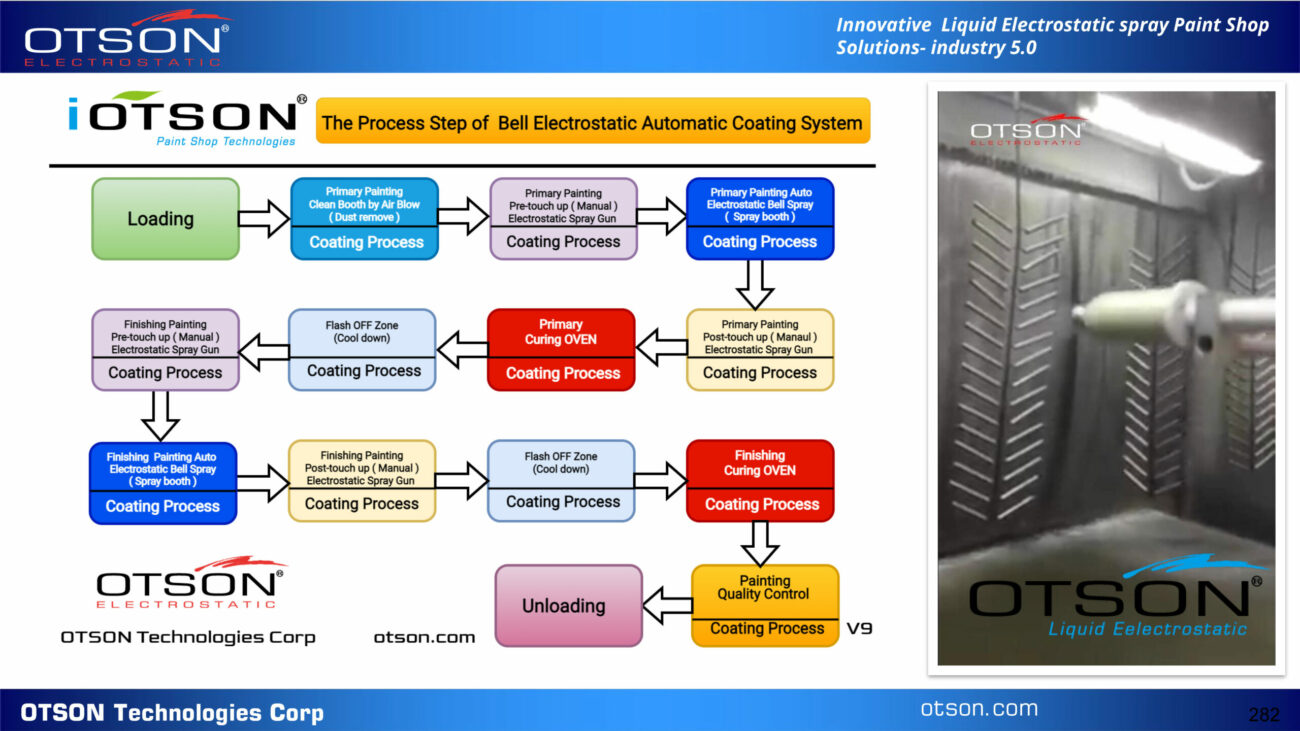
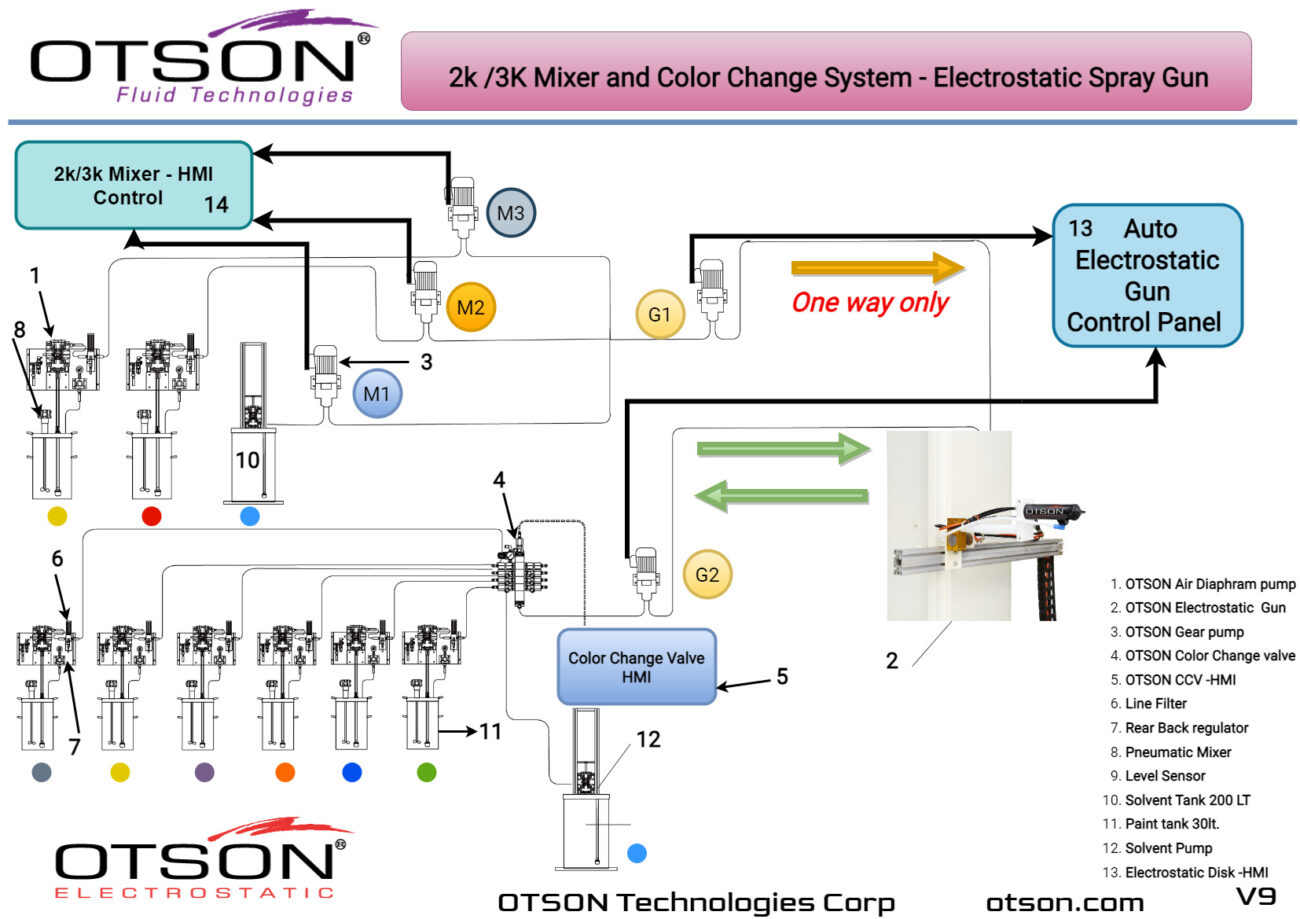
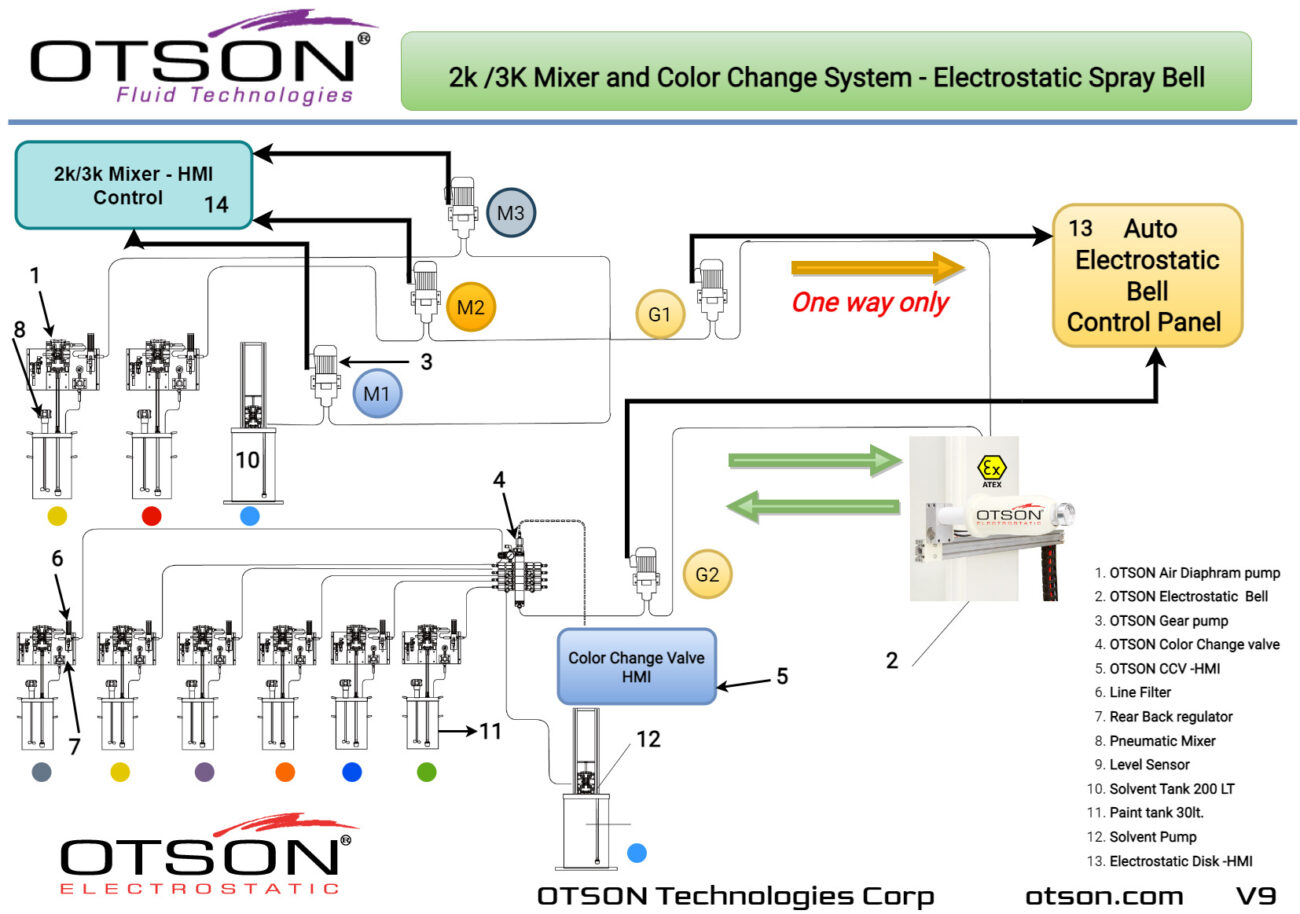
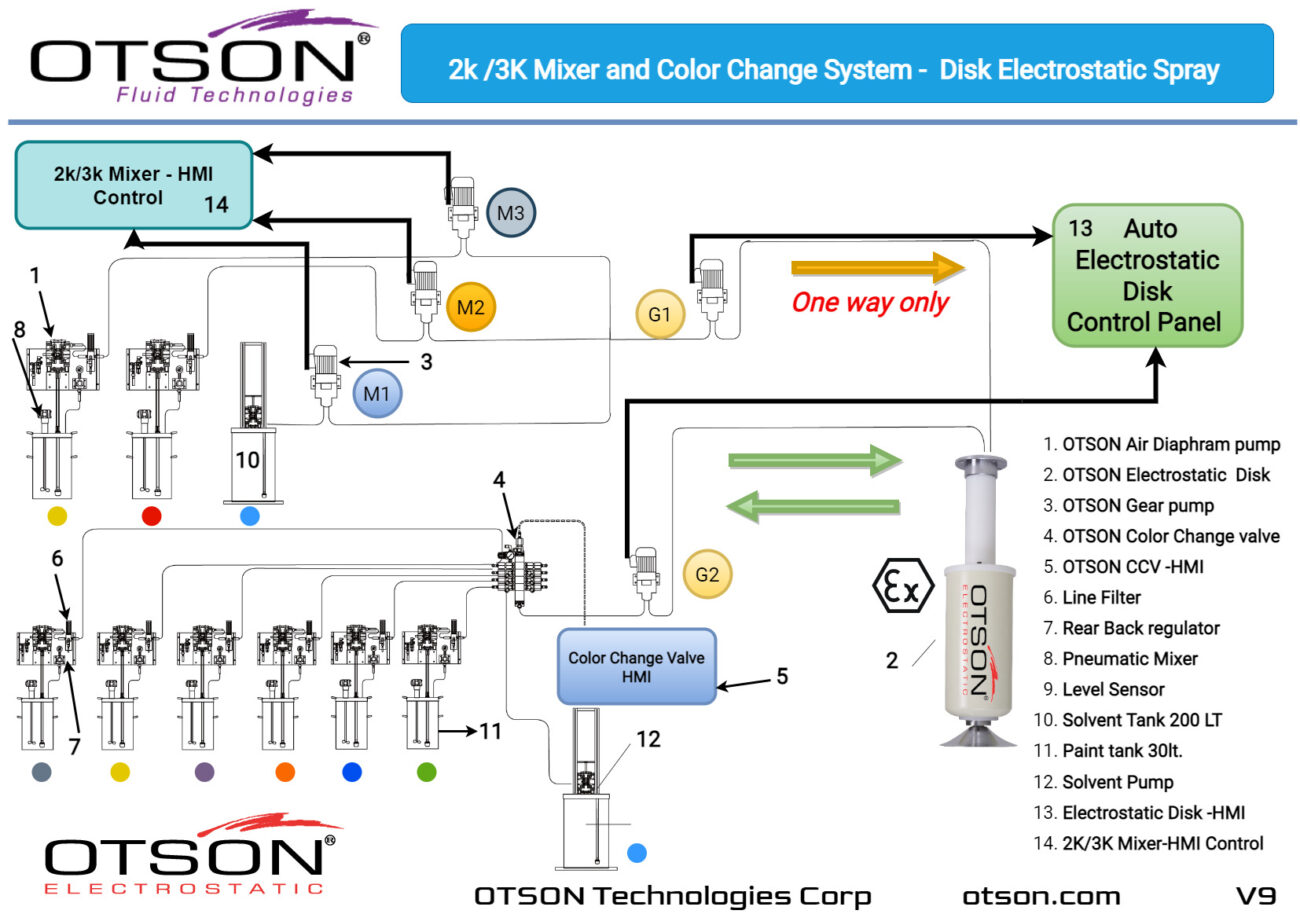
One of our flagship products is the OTSON Liquid Electrostatic, which features innovative technology and patented designs for electrostatic liquid coating and fluid transfer applications. Our product range includes a wide variety of equipment options such as disc and bell systems that cater to the unique requirements of various industries and applications.
OTSON Liquid Electrostatic systems are renowned for their precision, high efficiency, and reliability. Our products are specifically designed to minimize paint waste and increase production rates, resulting in a significant return on investment for our customers. Furthermore, our systems meet industry safety standards with ATEX certification, ensuring the delivery of high-quality finishes to our clients.
At OTSON, we understand the significance of offering complete solutions to cater to the diverse needs of our clients. Therefore, we are committed to integrating our OTSON Liquid Electrostatic systems with our smart paint shop solutions that provide greater process control, enhanced efficiency, and improved quality.
If you are looking for a reliable and efficient liquid electrostatic coating system, OTSON’s OTSON Liquid Electrostatic line is the perfect choice. Get in touch with us today to learn more about our products and services, and how they can benefit your business.
There are several advantages to using electrostatic spray coating over traditional spraying methods:
Electrostatic spray coating is a popular choice for mass production factories due to the many benefits it offers over traditional coating methods. Some of the key advantages of using electrostatic spray coating include:
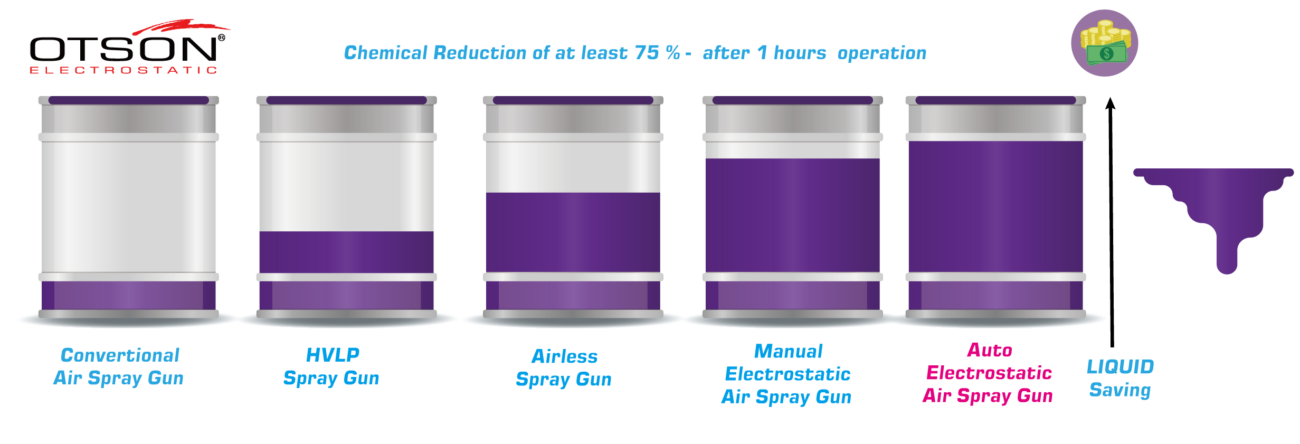
- High Spray Efficiency: Electrostatic spray coating is highly efficient, requiring less material to achieve the desired coating thickness. This leads to cost savings and reduced waste.
- Uniform Coating: Electrostatic spray coating creates a uniform coating on the surface of the product, thanks to the electrostatic charge that attracts the coating material to the surface. This ensures even distribution, resulting in a higher quality finished product with fewer defects.
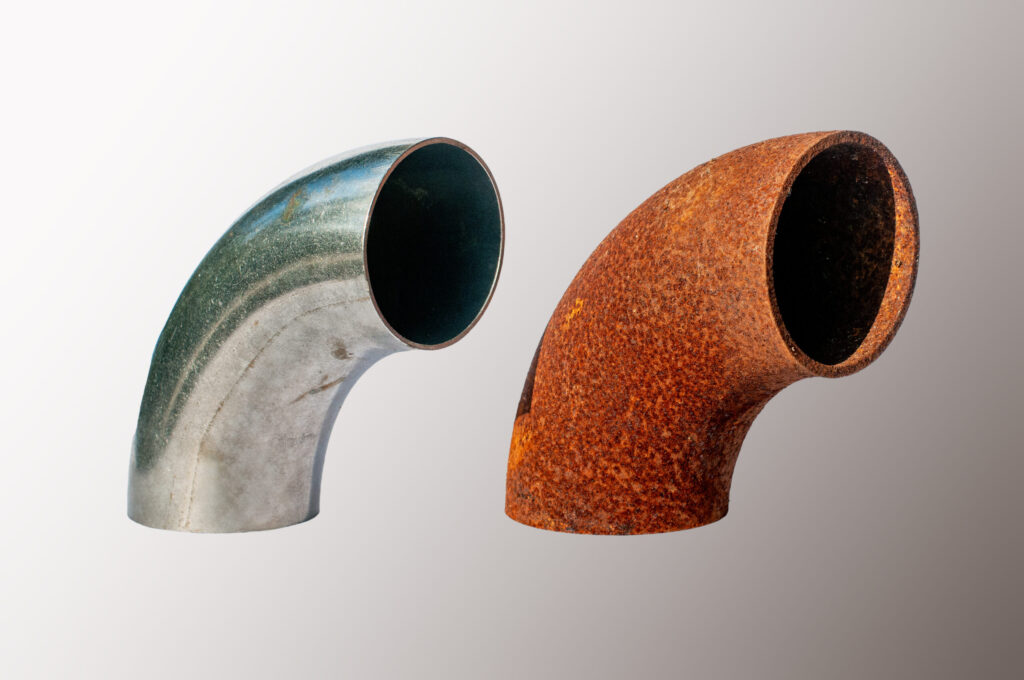
- Lower Environmental Impact: Electrostatic spray coating has a lower impact on the environment than some traditional coating methods. It produces less air and water pollution and can be used in enclosed areas with proper ventilation, reducing the amount of overspray and waste.
- Advancements in Electrostatic Coating Equipment: In recent years, there have been significant advancements in electrostatic coating equipment. High-voltage electrostatic generators, new structures for electrostatic spray guns, and new automatic control panels have enhanced the reliability and efficiency of the electrostatic coating process, providing a solid foundation for its continued development and implementation in various industries.
Overall, electrostatic spray coating is a versatile, efficient, and sustainable method that is widely used in various industries, including automobiles, bicycles, wheels, instrumentation, electrical appliances, agricultural machinery, household electrical appliances, daily hardware, steel furniture, doors, windows, power tools, toys, gas appliances, and other industrial fields. The benefits of electrostatic spray coating make it an ideal choice for businesses looking to improve their coating processes, reduce costs, and increase efficiency while reducing their environmental impact.