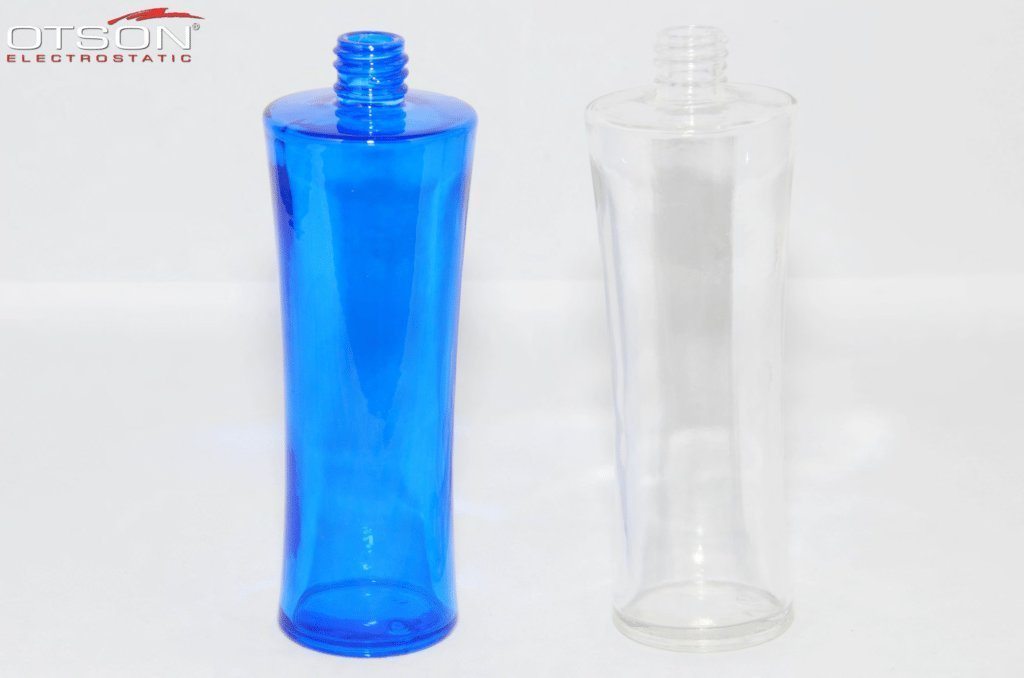
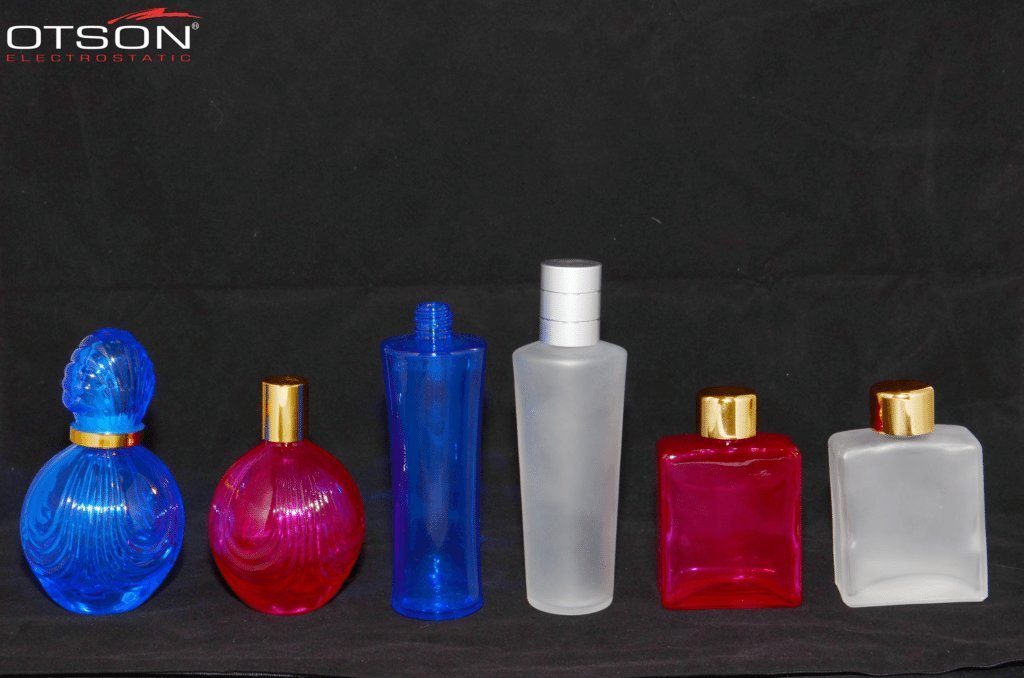
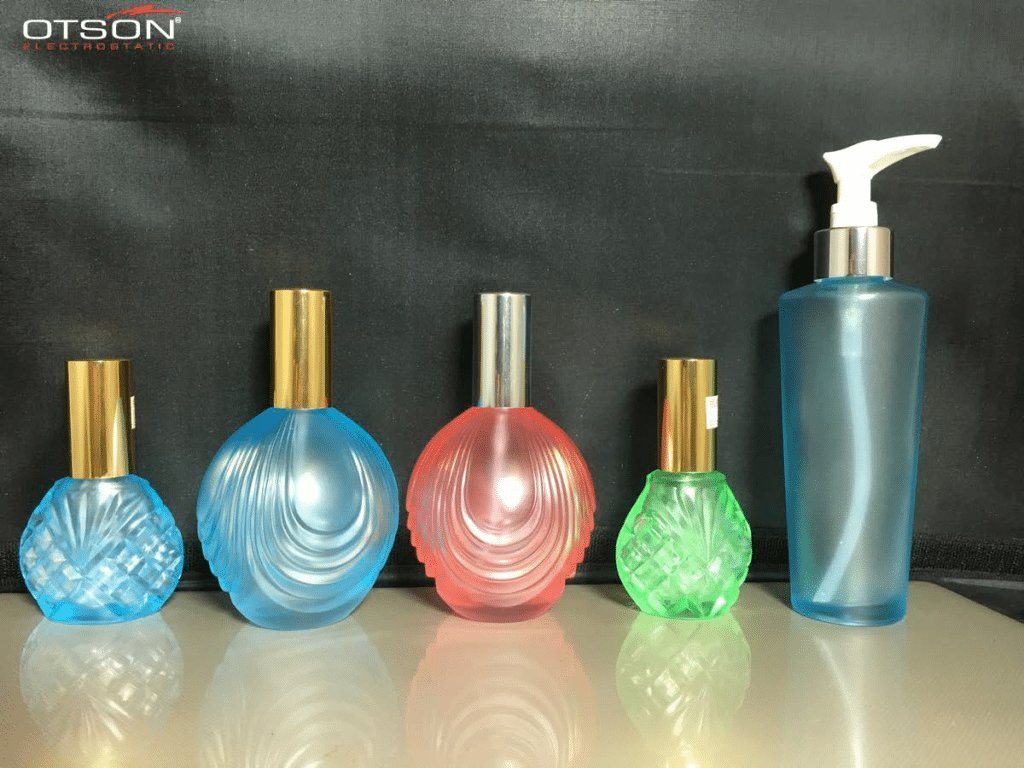
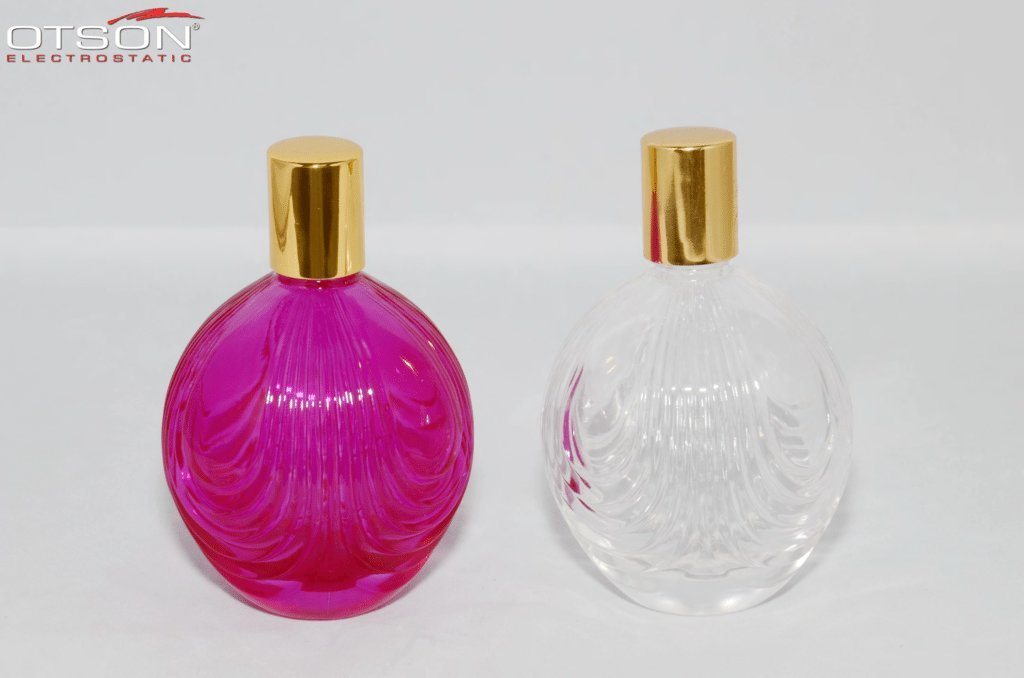
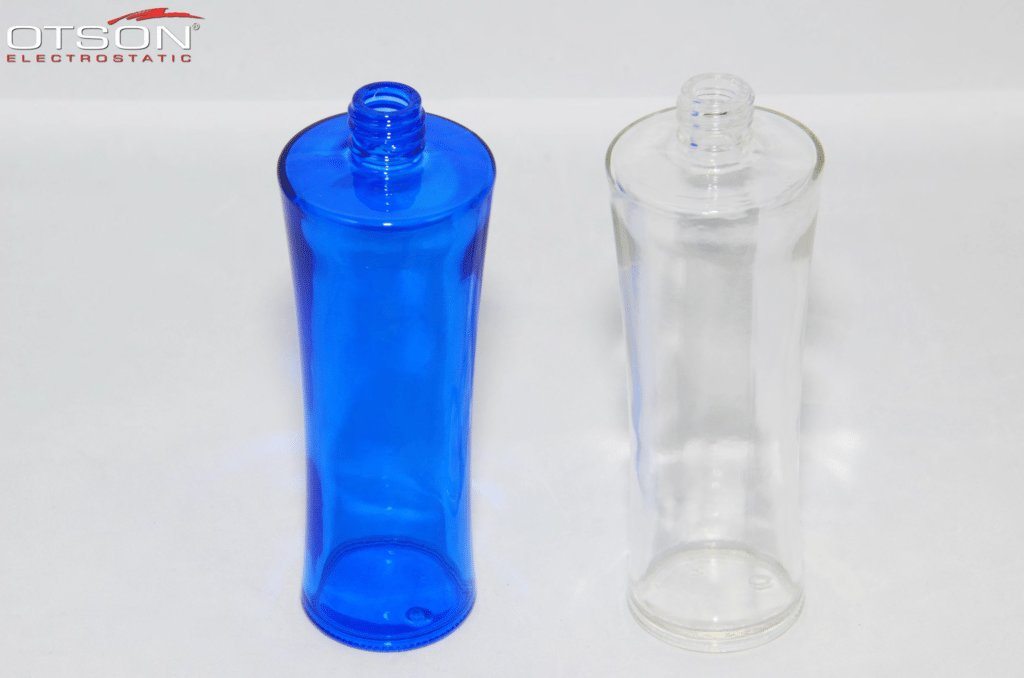
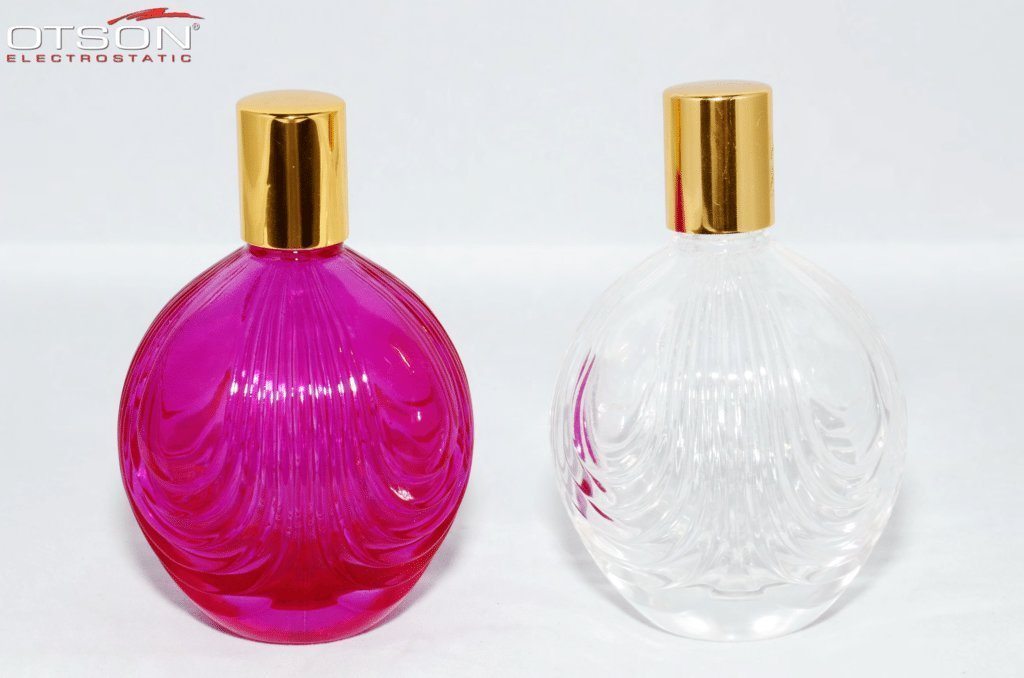
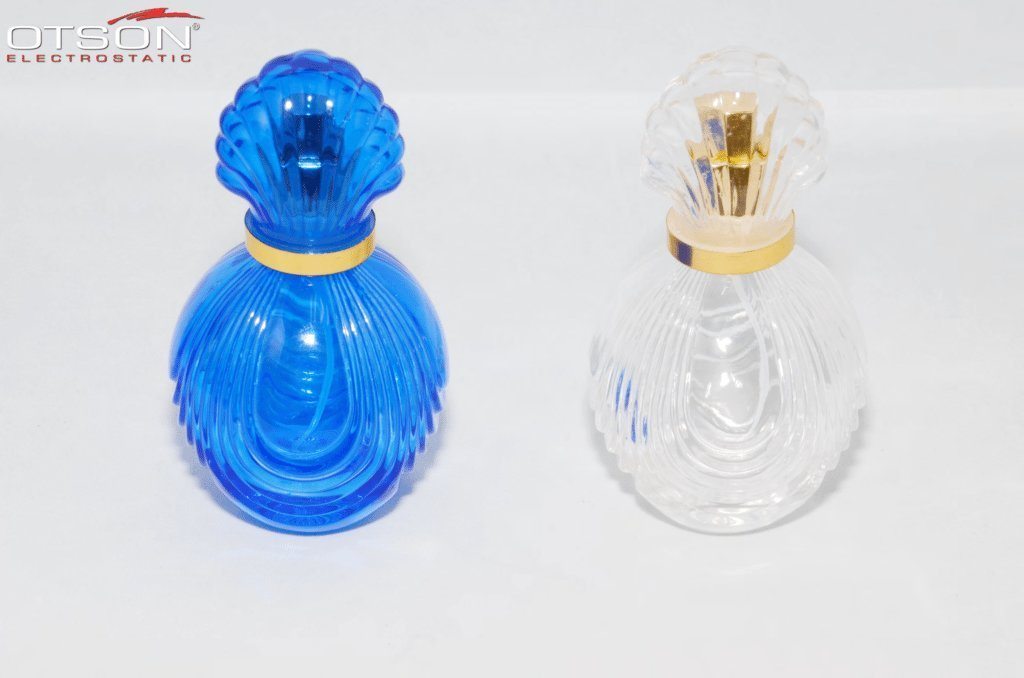
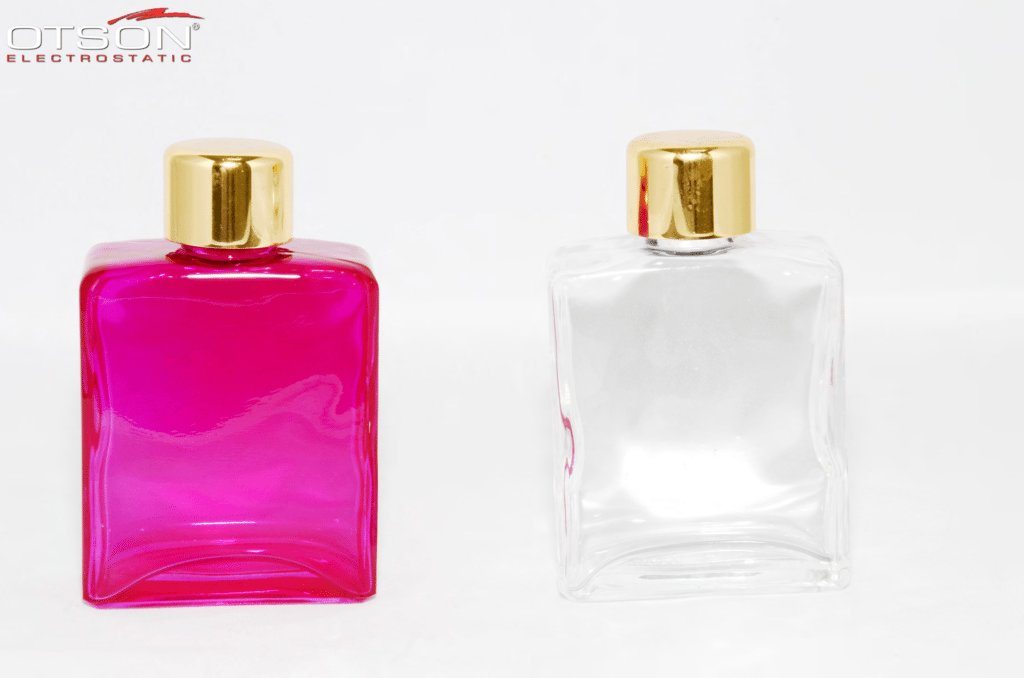
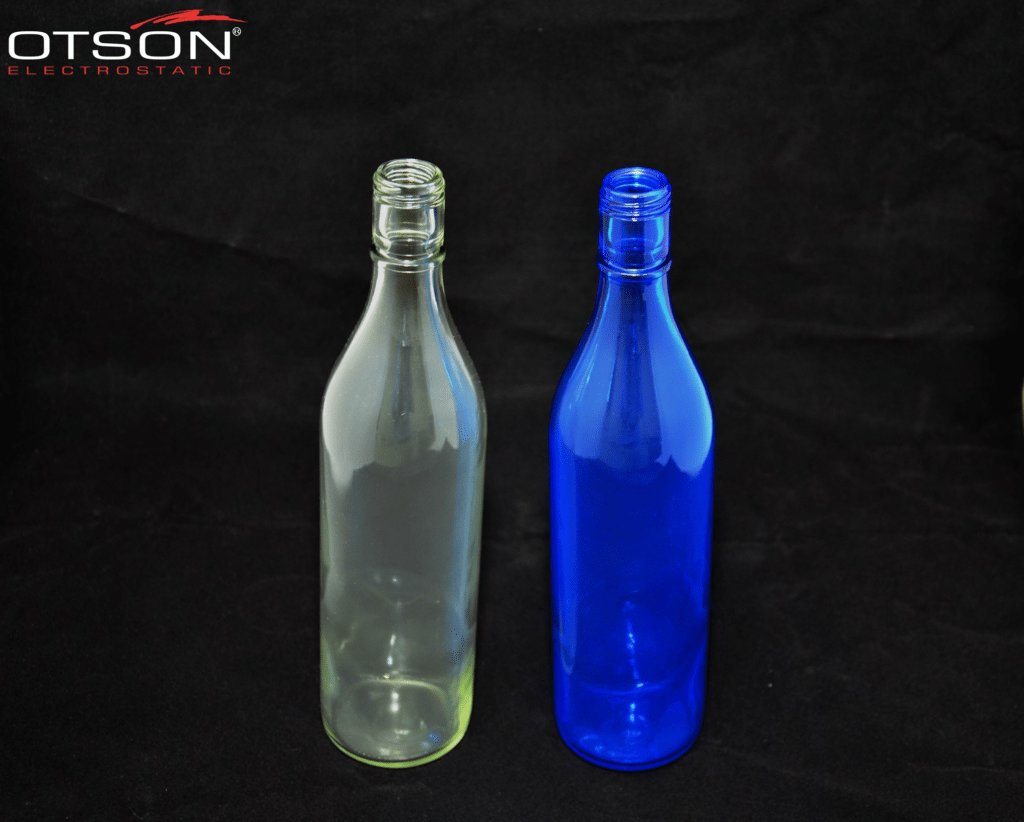
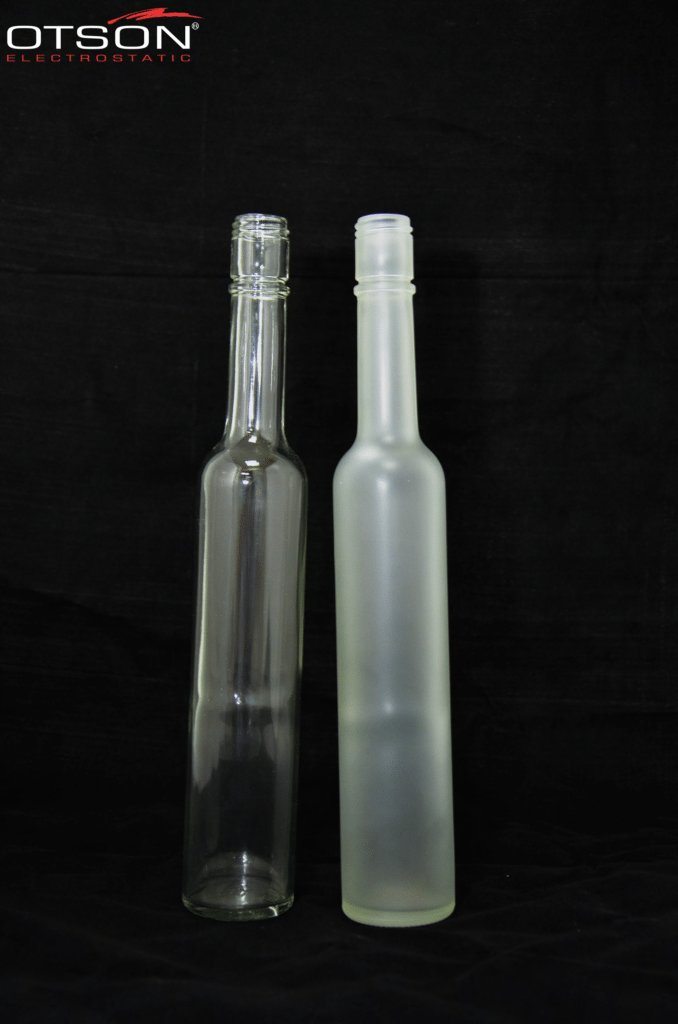
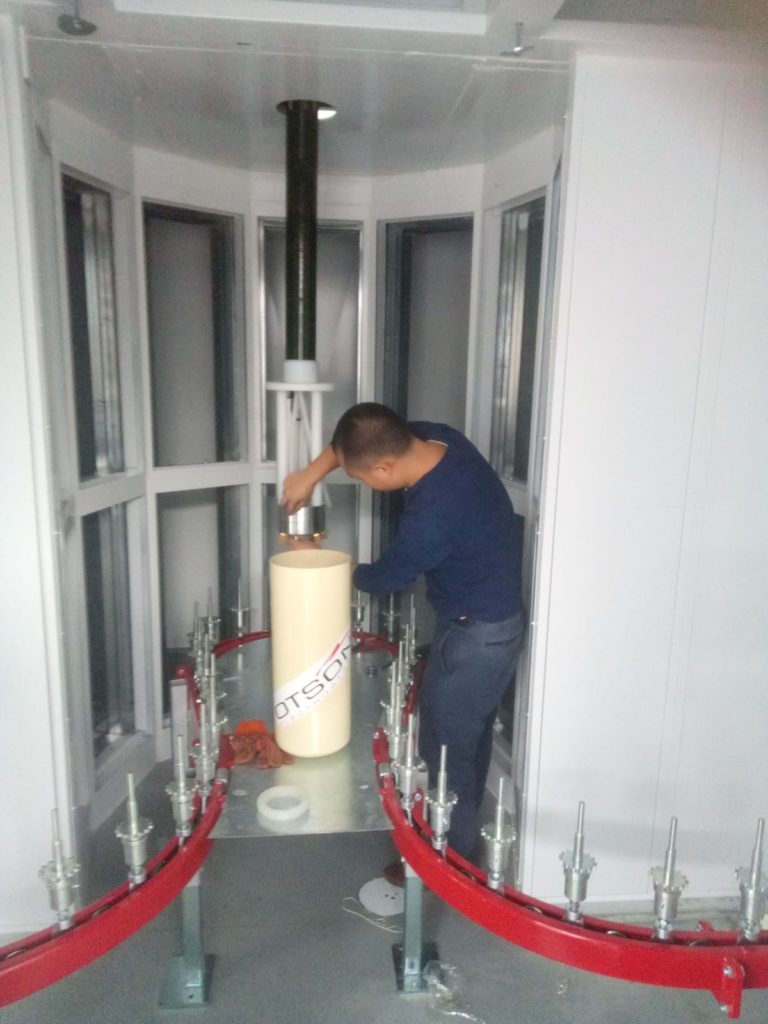
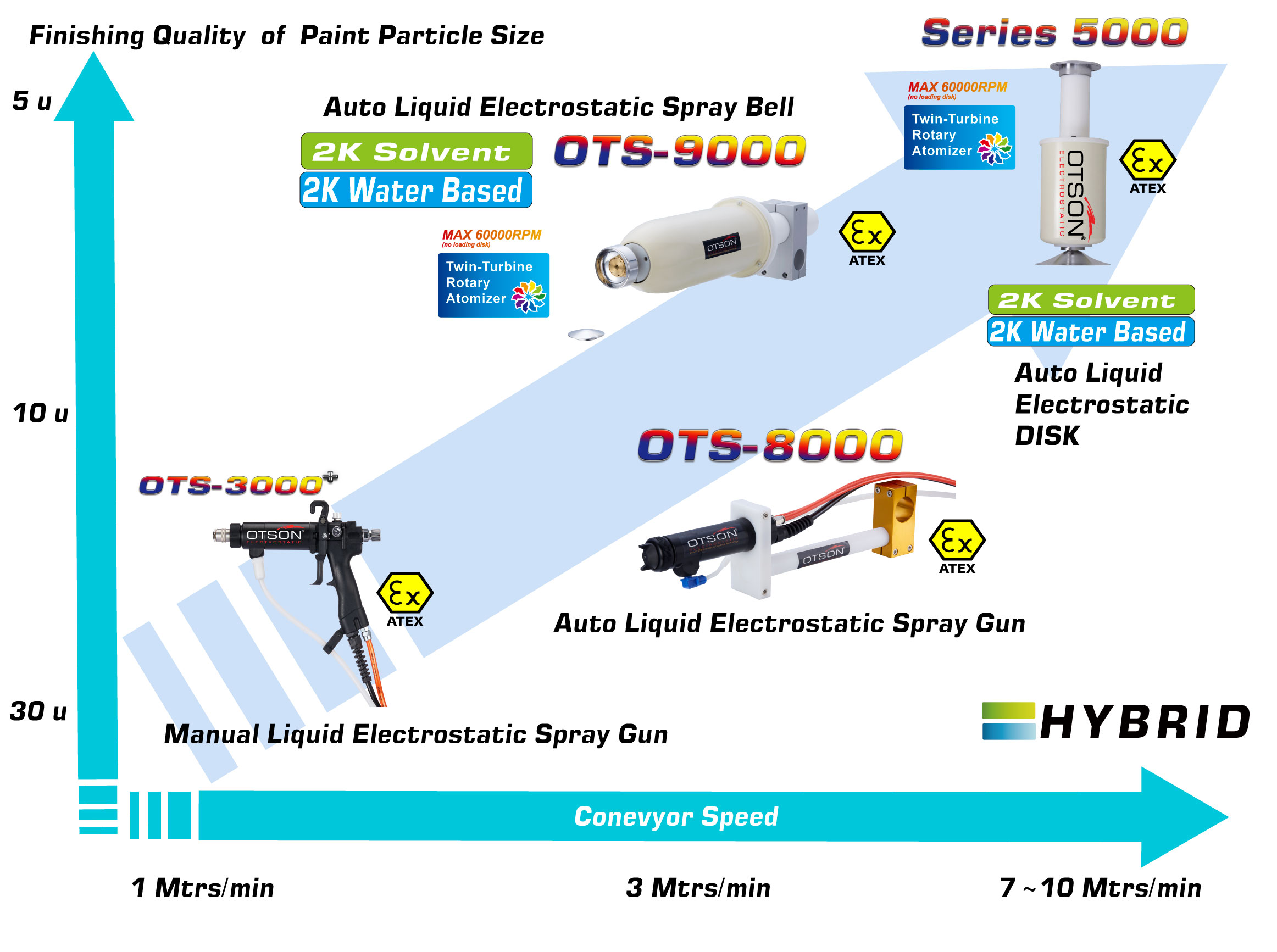
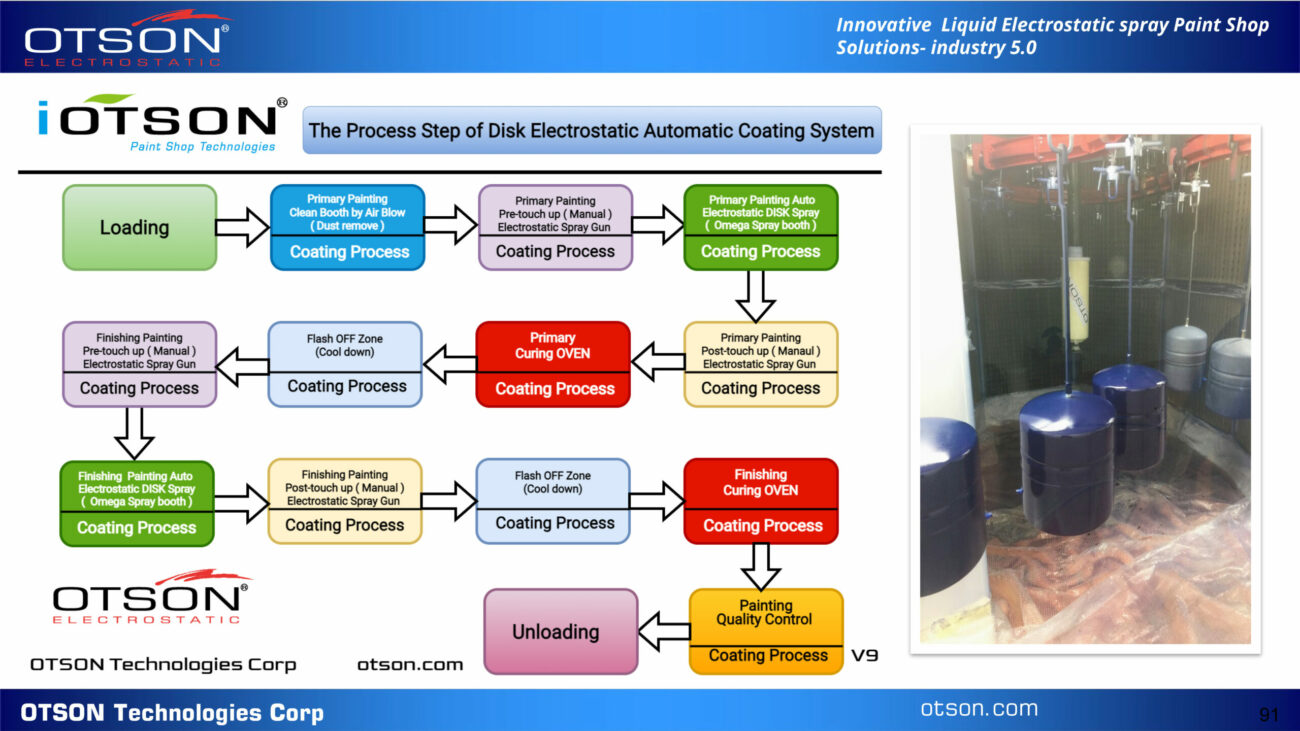
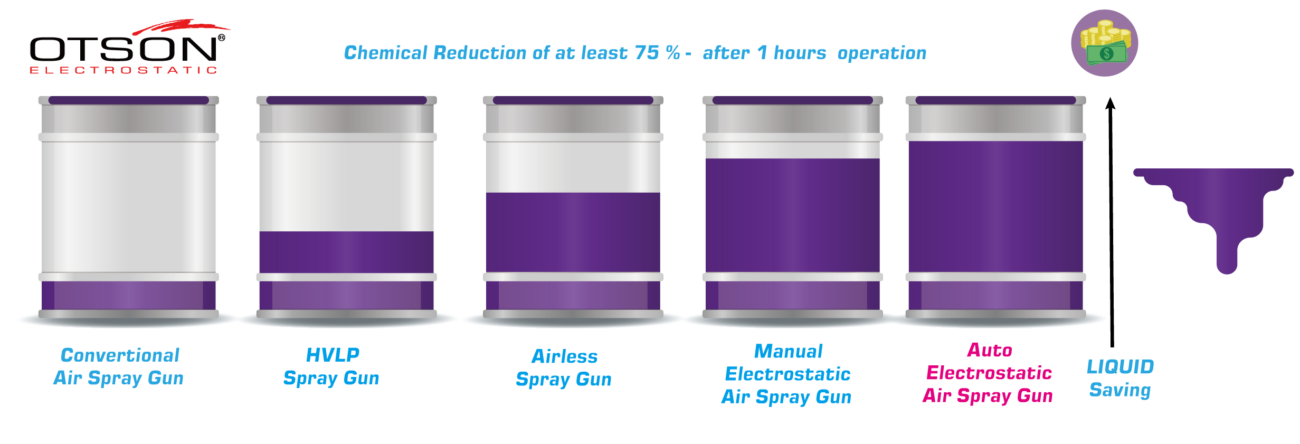
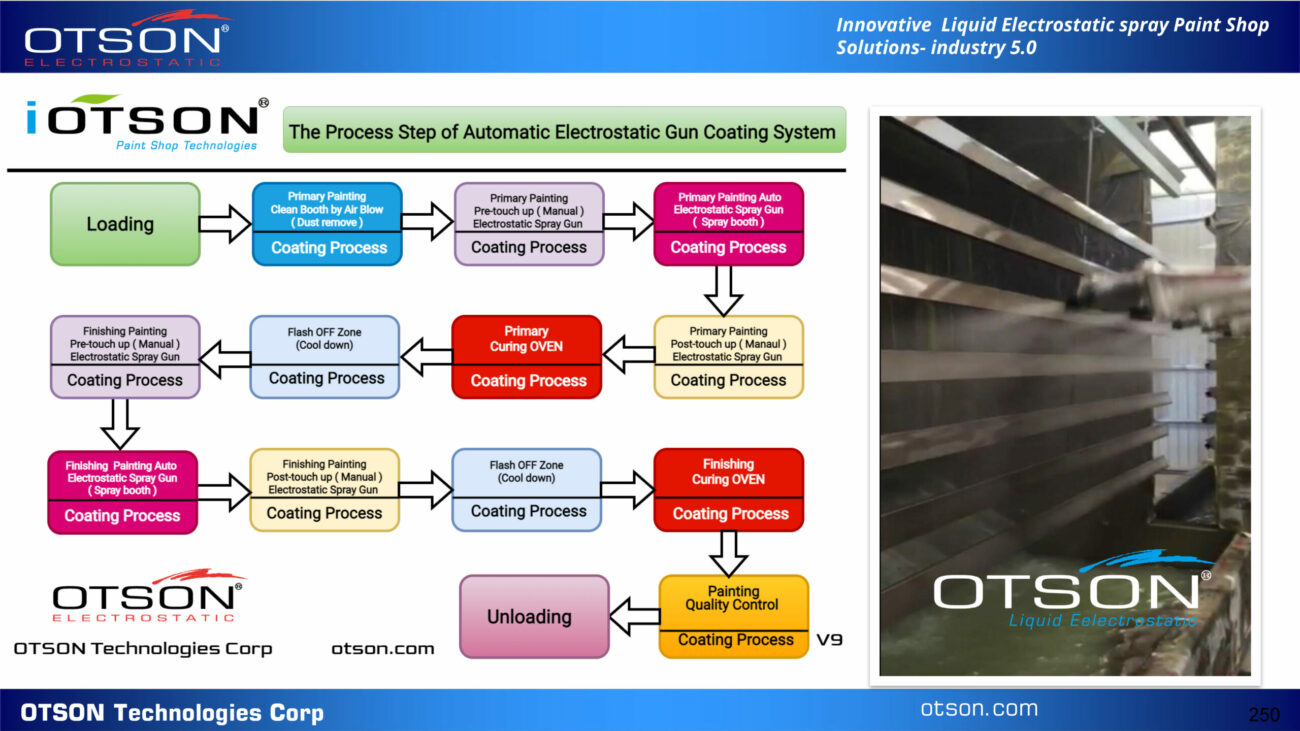
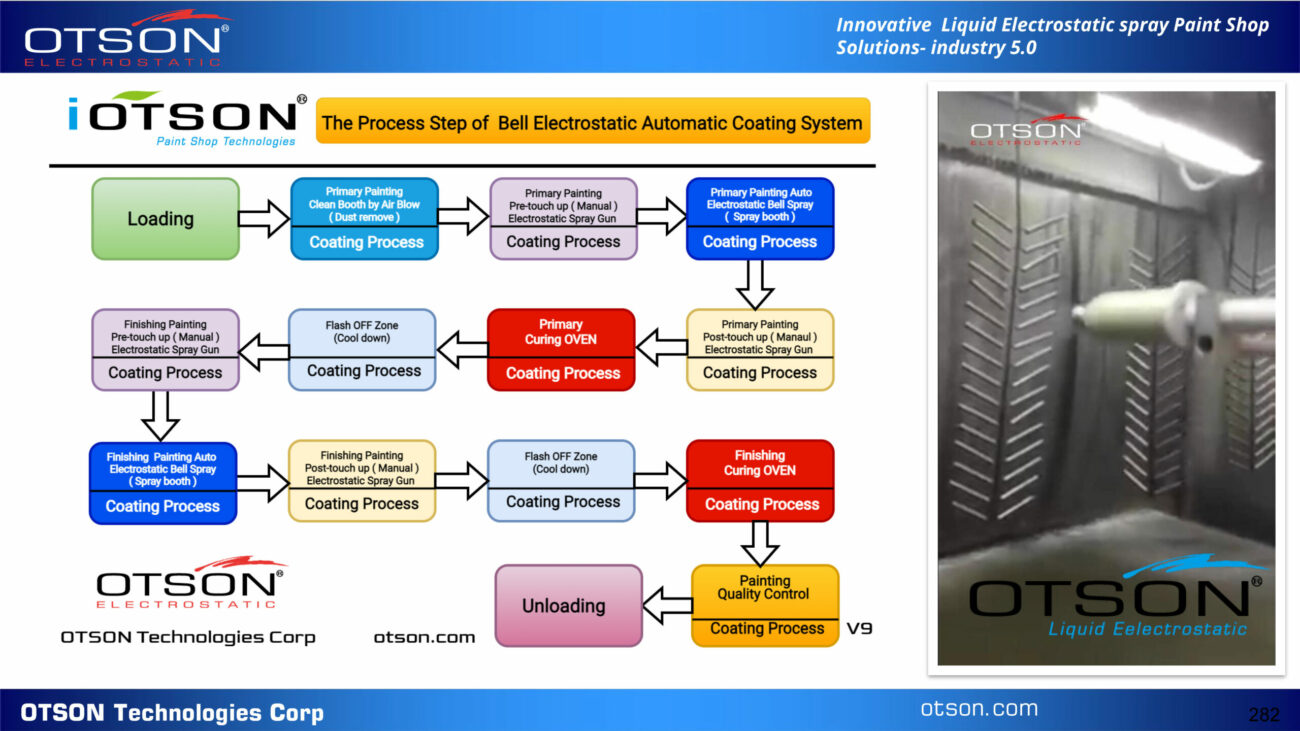
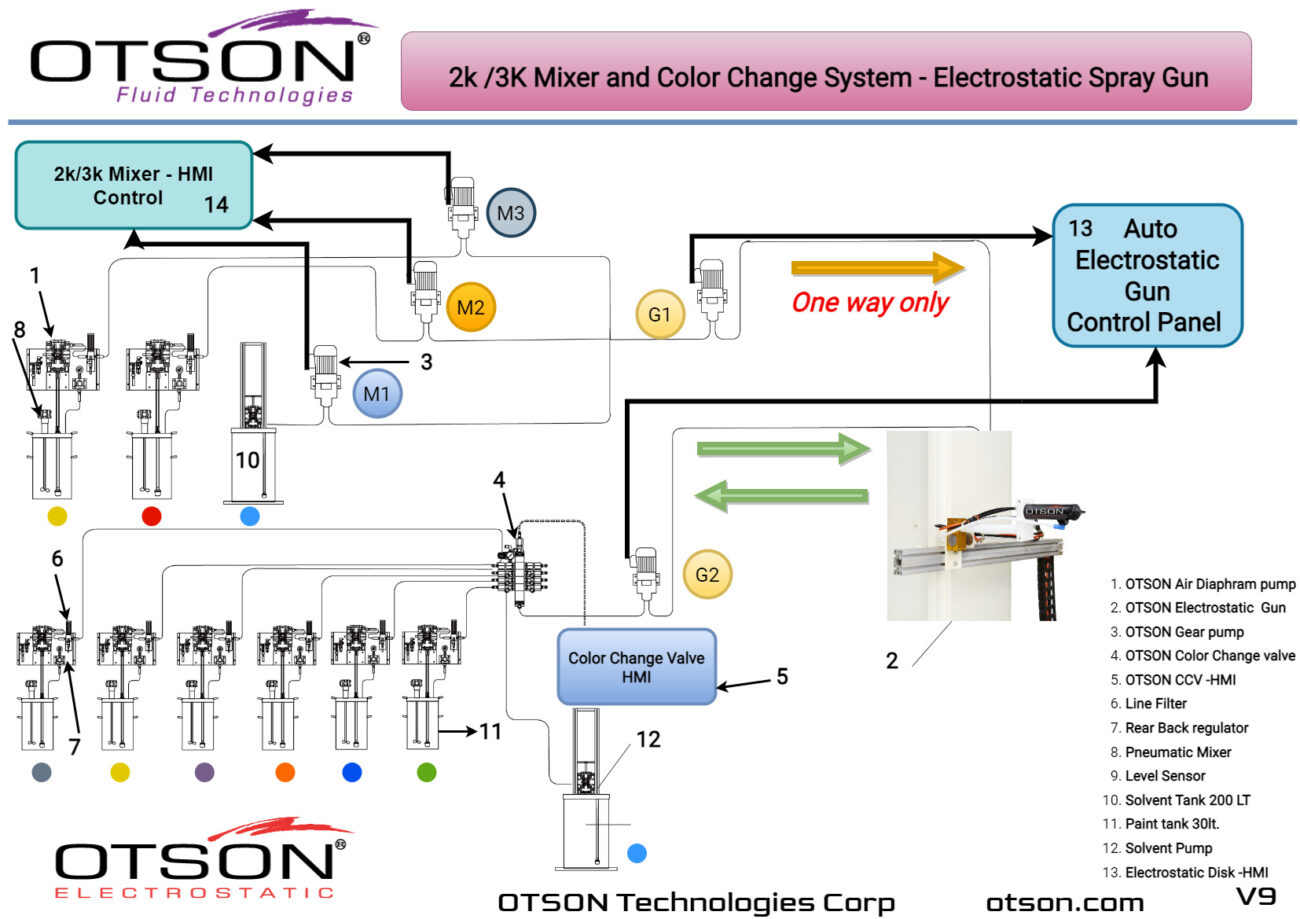
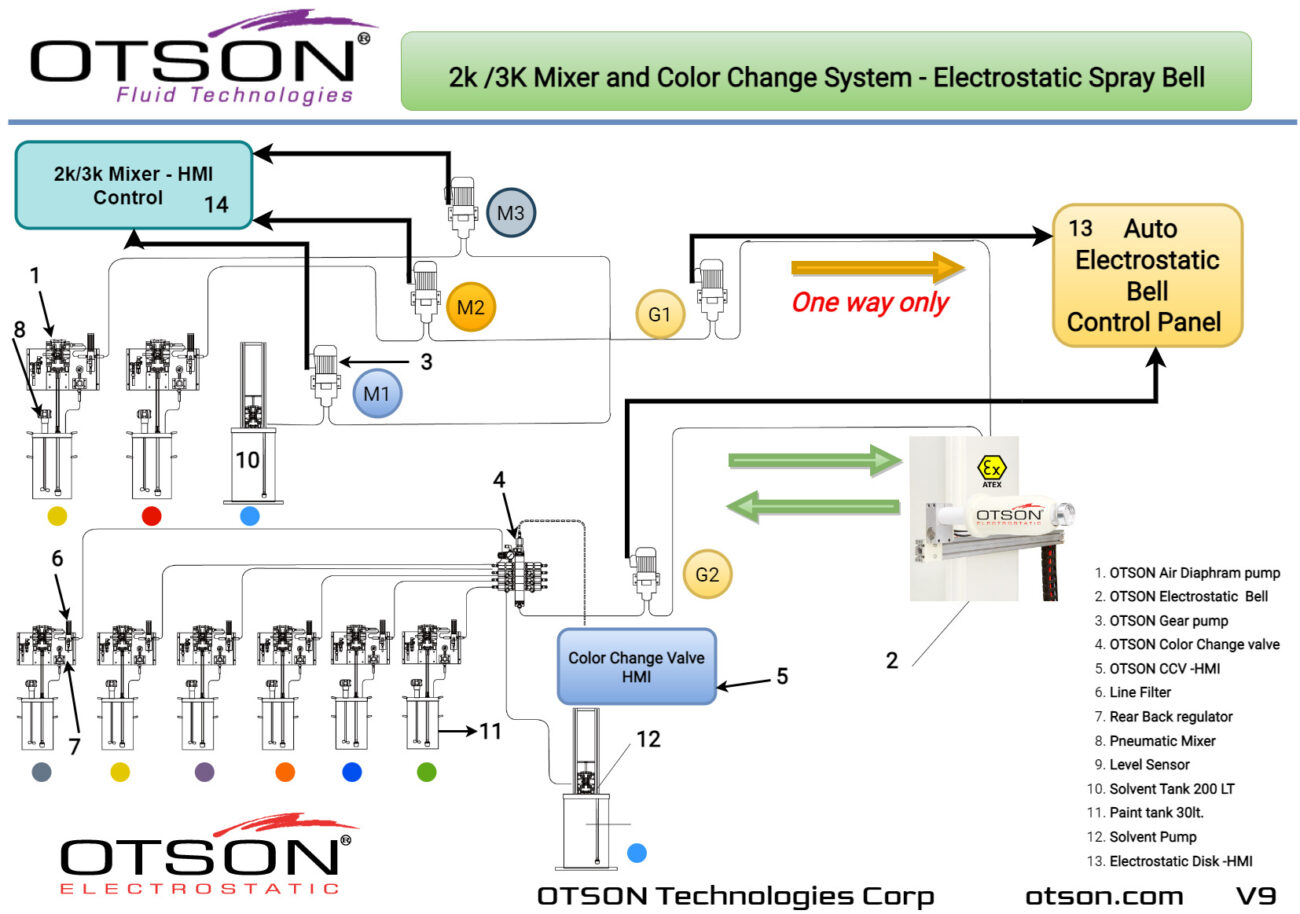
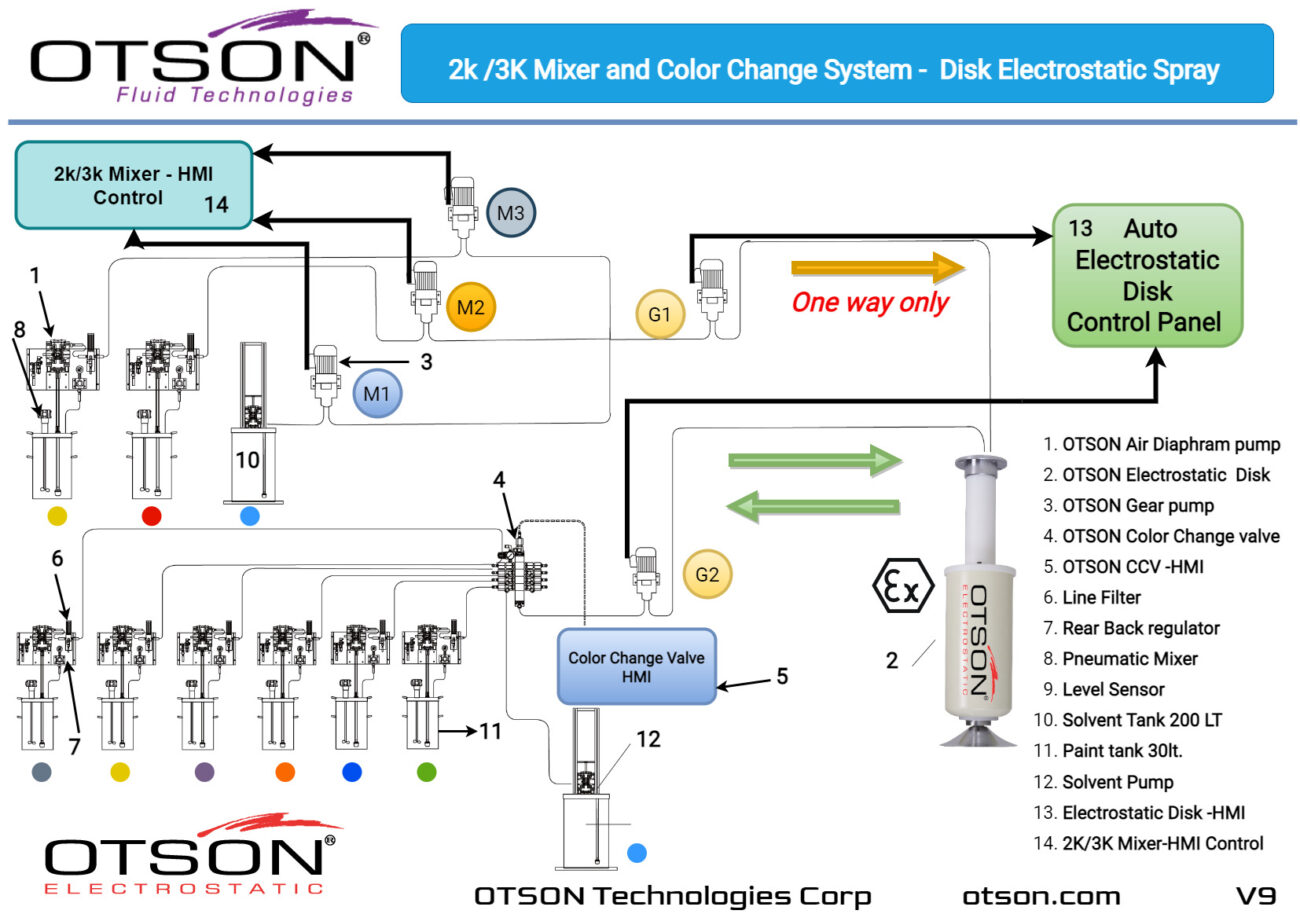
Liquid electrostatic spray technology is a method of applying thin, uniform coatings of liquid onto glass surfaces using an electrostatic charge. The process involves charging the liquid with an electrostatic field, which causes the droplets to become highly charged and repel each other. This results in a fine mist of charged droplets that are attracted to the grounded glass surface, creating an even and controlled coating.
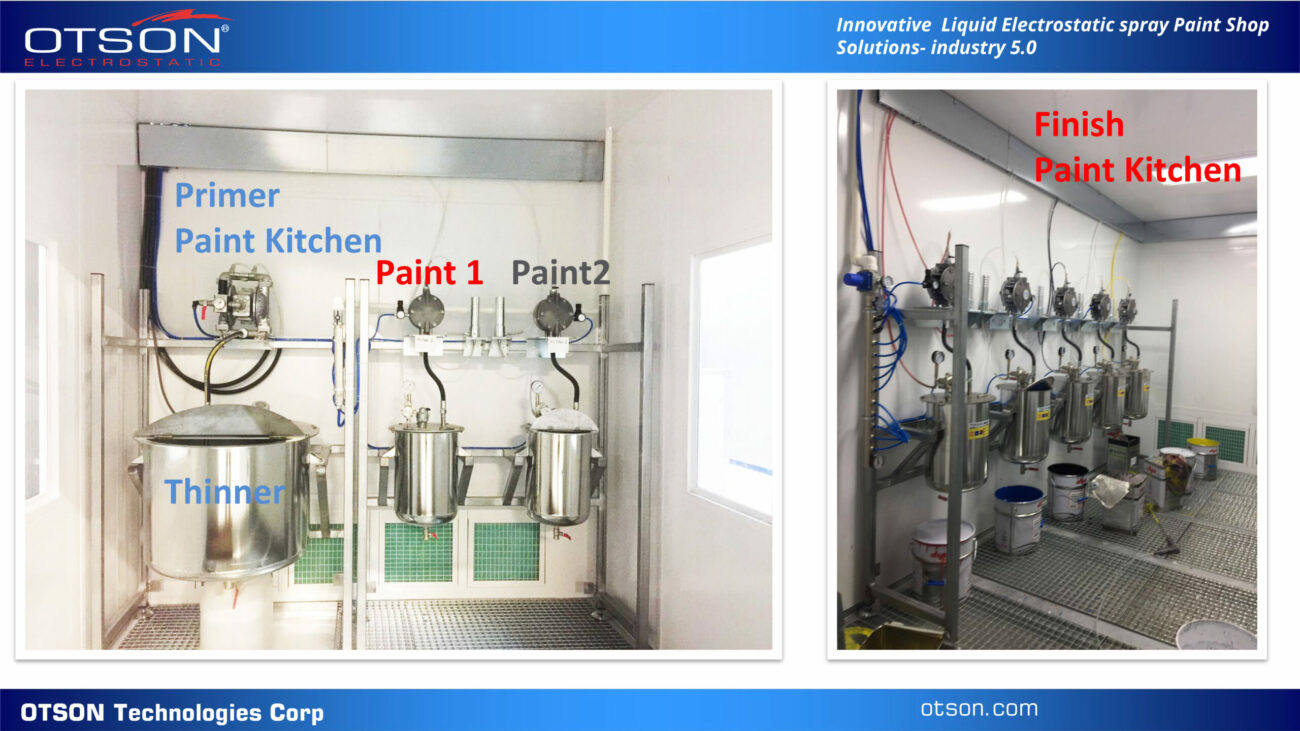
In the glass industry, liquid electrostatic spray technology is commonly used to apply solvent and water-based paints to glass surfaces. Solvent-based paints are typically used in the automotive and industrial industries, while water-based paints are used in the architectural and interior design industries.
Solvent-based paints are composed of organic solvents, resins, and pigments, and are used to create durable, scratch-resistant coatings on glass surfaces. These coatings are also resistant to chemicals and can withstand high temperatures.
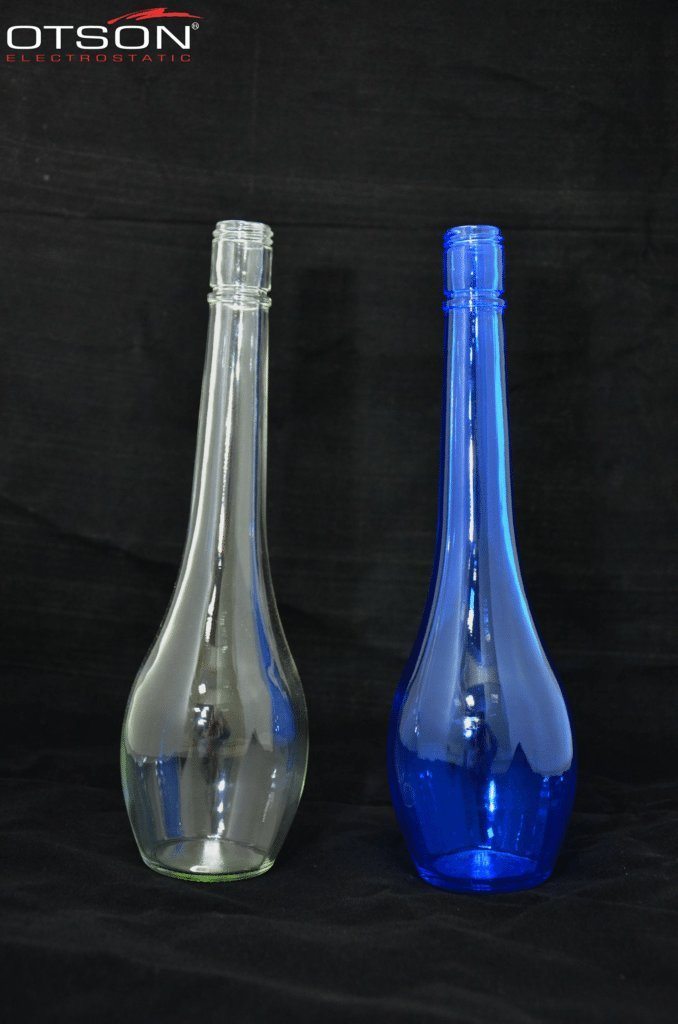
Water-based paints are composed of water, resins, and pigments, and are used to create decorative coatings on glass surfaces. These coatings can be used to create different colors, textures, and patterns on the glass, and can also be used to create functional coatings, such as low-e and self-cleaning coatings.
Liquid electrostatic spray technology can also be used to apply coatings of functional materials onto glass surfaces, such as anti-reflective coatings, low-e coatings, and self-cleaning coatings. These coatings can help to improve the energy efficiency and functionality of the glass, which is important for a variety of applications, including windows, doors, and skylights.
Overall, liquid electrostatic spray technology is a versatile and effective way to apply solvent and water-based paints, as well as functional coatings, to glass surfaces. It is becoming an increasingly popular choice in the glass industry due to its ability to create precise and consistent coatings, as well as its efficiency and cost-effectiveness.